Cardiac Rhythms and Arrhythmias-
Recognition
Recognition
**Think about the causes and treatments for all of the following. Medications, interventions, etc.
Normal Sinus Rhythm:
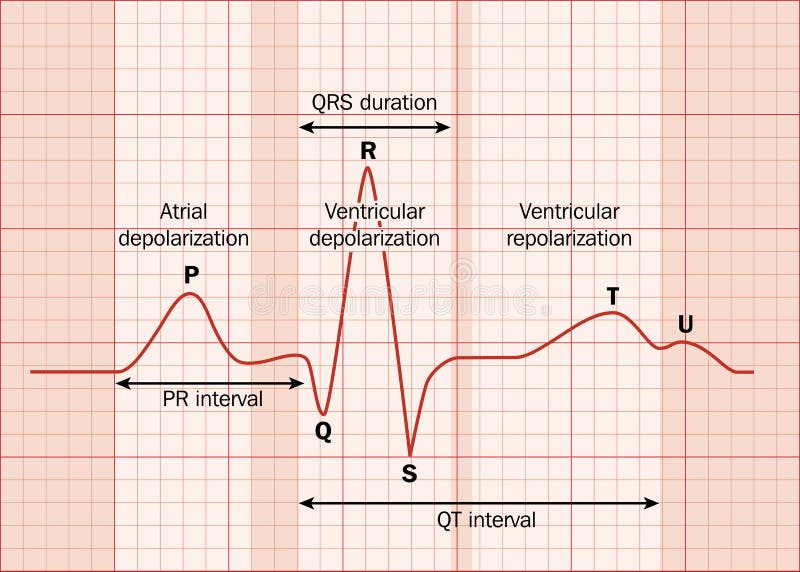
Rate 60-100bpm in adults, regular rhythm, p-wave present before every QRS complex
Sinus Bradycardia:
Rate less than 60bpm in adults, regular rhythm, p-wave present before every QRS complex
Sinus Tachycardia:
Rate 100-150bpm in adults, regular rhythm, p-wave present before every QRS complex
Atrial Fibrillation:
Rate is variable, irregular rhythm, difficult
Atrial Flutter:
Rate is regular (can be fast or slow), regular rhythm. Classic "saw tooth pattern"
Supraventricular Tachycardia:
Rate >150bpm, regular rhythm, unable to identify p-waves due to high rate
Second Degree AVB
-Type 1 (Wenkebach)" Going, Going, Gone" or "Longer, longer, longer, drop, now you have a wenkebach". PR prolongation leads to a dropped QRS.


-Type 2 (Mobitz Type II)PR interval is the same, however not every p-wave has a QRS complex following it.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zqmag9LEHcc
And check out the AV Block Family Poem here: https://nursingnotes.co.uk/the-story-of-the-av-block-family/
And check out the AV Block Family Poem here: https://nursingnotes.co.uk/the-story-of-the-av-block-family/
Ventricular Fibrillation:
(fine or coarse)
Ventricular Tachycardia:
Torsades de pointes (polymorphic VT)
Asystole:
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA):
The electrical conduction system in the heart is still working, but the pump or mechanical system has failed. The patient will have no pulse.
**Can be any of the above strips (except asystole) and the patient has no pulse.
**Can be any of the above strips (except asystole) and the patient has no pulse.
Acute Myocardial Infarctions
Anterior Wall MI:The anterior wall is affected by the LAD, Left main and circumflex arteries. You will see ST elevations in V3 and V4 with reciprocal changes in inferior leads (II, III, avF). If lateral wall is involved you will see changes in V5 and V6 and if septum is involved changes are visible in V1 and V2. This supplies blood to the musculature of the left ventricle and anterior -septum.
What type of arrhythmia would you expect to see? Why?
How would it be treated?
With our treatment, what would we be cautious of and why?
Inferior Wall MI:
The inferior wall is affected by the right coronary artery. You will see ST elevations in leads II, III, aVf with reciprocal changes in leads V3 and V4. It perfuses the SA node, AV node and proximal bundle of his.
What type of arrhythmia would you expect to see? Why?
How would it be treated?
With our treatment, what would we be cautious of and why?
How are Acute ST- Elevation Myocardial infarctions diagnosed?
EKG! Should be done immediately, but must be done within 10 minutes of arrival.
What nursing interventions would you perform? Labs needed? Medications? Patient education?
EKG! Should be done immediately, but must be done within 10 minutes of arrival.
What nursing interventions would you perform? Labs needed? Medications? Patient education?
For additional Information:
This presentation explains STEMI's and focuses on the vessels affected as well as which ECG leads help diagnose.
This explains rhythm interpretation: